第8章 数据库空间管理 320
8.1. 数据文件的空间使用和管理 321
·
数据文件类型:mdf and ldf
·
数据文件Name:Name and Physical_Name
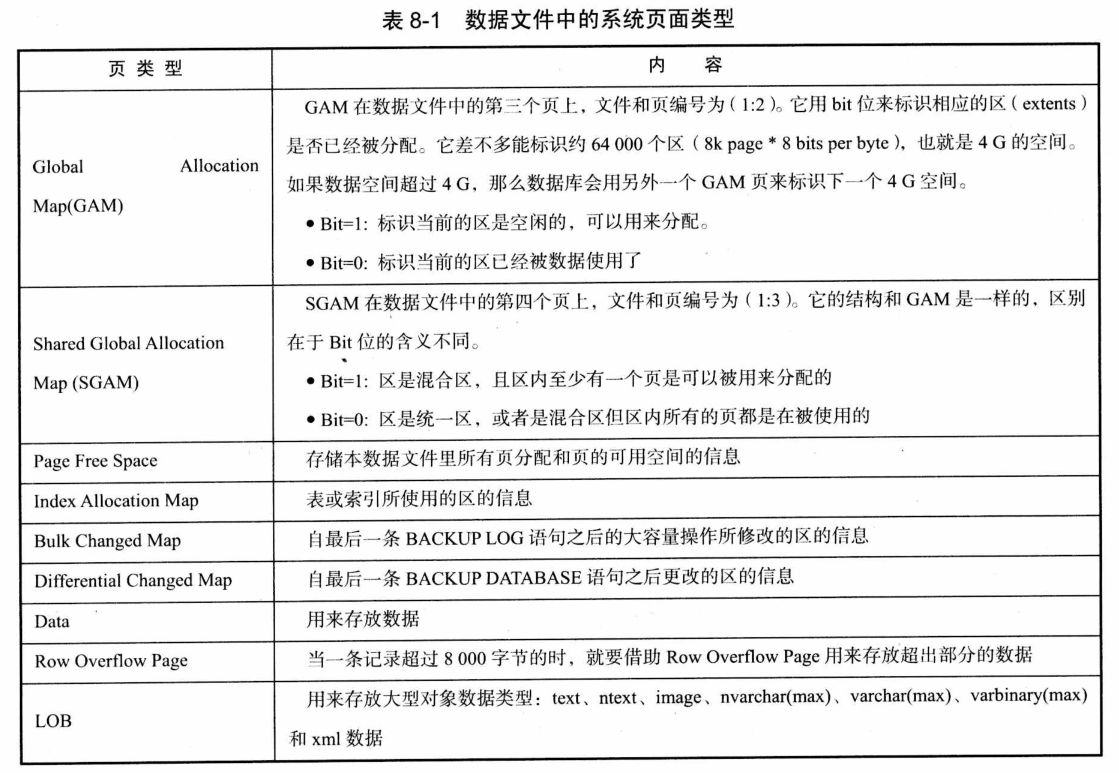
8.1.1. 数据文件存储结构 321
·
By Page, Extent
·
Different types of pages in SQL
Server
(one possible
page structure of a database file)
8.1.2. 表存储结构 323
·
Table organization – A
table has one or more partitions. Each partition can have up to 3 allocation
units (Data, LOB, and Row-Overflow), and each allocation unit can have multiple
pages.
·
Table has no indexes (Heap) –
navigate via the Index Allocation Page.
Heaps have one row in sysindexes with indid = 0. The column sysindexes.FirstIAM points to the first IAM page in the
chain of IAM pages that manage the space allocated to the heap. Microsoft® SQL
Server™ 2000 uses the IAM (Index
Allocation Map) pages to navigate
through the heap. The data pages and the rows within them are not in any
specific order, and are not linked together. The only logical
connection between data pages is that recorded in the IAM pages.
·
Table has a non-clustered index: (1)
每个NCI,都有一个相对应的Partition,(2)
the data is stored in one place, the index in
another, with pointers to the storage location of the
data. (3) The items in the index are organized in a B-tree structure. On the
top is the root-index, and the bottom is the leaf-node of the index, which
contains the file number, page number, and slot number of the row. The leaf-node of the NCI point to the actual
data. (4) The data is stored as a heap.
·
Table has clustered index – the
leaf-nodes of the index contain the actual data, rather than pointers as in NCI
·
Case study – using DBCC Page to
trace on the storage structure of data via a non-clustered index
8.1.3. 比较存储结构对空间使用的影响 332
·
Non-clustered index
needs extra space to store the B-tree information
·
The authors
demonstrated the size of the table is the same in the heap and clustered
structure. But remember, the clustered index also takes extra space, which is
not discussed.
·
Storage space is not
the major concern in my opinion.
8.2. 日志文件的空间使用和管理 337
·
日志文件不以页、区为存储单位,而是以日志记录(Log Record)作为存储单元。
·
一个Physical Log
File contains many VLF. 一个VLF有很多块,一块里又有很多Log Records.每个Log Record都有一个LSN(Log Sequence
Number)。顺理成章地,这个LSN有三部分组成:VLF的序列号,VLF中的块的编号,和块中日志记录的编号。例如:0000001D:000000FD:0002
·
Log File是一种回绕的文件。
When the end of the logical log
reaches the end of the physical log file, the new log records wrap around to
the start of the physical log file.
·
查看Log内容
o DBCC Log
o ApexSQL Log
·
日志文件的特点
o The
log content contain data and meta data, but not the commands causing the data
changes.
o The
contents are meaningful to SQL Server, but not meaningful to human beings.
o One
row change may have multiple records in the log file
o We
can find the beginning and ending time, but we do not know who and what causes
the changes from the log records. If you need to track who makes the changes,
use SQL Trace or Events, not DBCC LOG.
o The
log records contain the beginning and ending status of the data, but not
the intermediate changes.
8.3. 空间使用计算方法 341
·
DBCC showfilestats (and the SQL Server Standard Reports)
·
EXEC sp_spaceused N'[HumanResources].[Employee]',@updateusage = N'TRUE';
·
sys.dm_db_partition_stats
·
sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats
(or DBCC SHOWCONTIG)
·
For Log Space: DBCC
SQLPERF(LogSpace)
8.4. tempdb的空间使用 346
8.4.1. How tempdb is used?
·
User Objects - User objects are explicitly created by the user. These objects
may be in the scope of a user session or in the scope of the routine in which
the object is created. A routine is a stored procedure, trigger, or user-defined
function. User objects can be one of the following:
o
User-defined tables and
indexes
o
System tables and indexes
o
Global temporary tables and
indexes
o
Local temporary tables and
indexes
o
Table variables
o
Tables returned in
table-valued functions
·
Internal Objects - Internal objects are created as necessary by the SQL Server
Database Engine to process SQL Server statements. Internal objects are created
and dropped within the scope of a statement. Internal objects can be one of the
following:
o
Work tables for cursor or
spool operations and temporary large object (LOB) storage.
o
Work files for hash join or
hash aggregate operations.
o
Intermediate sort results for
operations such as creating or rebuilding indexes (if SORT_IN_TEMPDB is
specified), or certain GROUP BY, ORDER BY, or UNION queries.
o
Each internal object uses a
minimum of nine pages; one IAM page and one eight-page extent.
·
Version
Stores - A version store is a collection
of data pages that hold the data rows that are required to support the features
that use row versioning.
There are two version stores: a common version store and an online-index-build
version store. The version stores contain the following:
o
Row versions that are
generated by data modification transactions in a database that uses snapshot or
read committed using row versioning isolation levels.
o
Row versions that are
generated by data modification transactions for features such as: online index
operations, Multiple Active Result Sets (MARS), and AFTER triggers.
·
Tempdb 空间使用跟踪
o
sp_spaceused以及它所依赖的sys.allocation_units和sys.partitions不能准确地反应出Tempdb 空间, 因为许多Internal Objects 和Row Versioning Objects得不到反映。
o
sys.dm_db_file_space_usage可以反映出三类Objects在tempdb上的使用情况。
·
Case Study – Which actions
cause the tempdb suddenly increasing?
o
SQL Trace – 影响性能
8.5. 数据文件的收缩 353
8.5.1. Is the space relieved after deletion? – It depends on whether
this is a cluster index on the table. If no CI, the empty pages are not
immediately relieved. But they will be re-used when new data are inserted. No
worries.
8.5.2. What
if I want to relieve the empty pages immediately?
·
Create or Rebuild the clustered
index
·
If no CI, move the data to a new
table, drop or truncate the old one.
·
You can use DBCC ShrinkDatabase or
DBCC ShrinkFile
8.5.3. How
to use DBCC ShrinkDatabase or DBCC ShrinkFile
·
首先,DBCC
ShrinkDatabase 一次影响所有文件包括日志文件,又不能指定每个文件的大小,所以,一般推荐使用DBCC
ShrinkFile。
·
MDF文件不能被清空,但可以被压缩。NDF文件可以被清空。
·
Target_Size不能大于文件中的Free Space
·
DBCC ShrinkFile可以清空文件(DBCC SHRINKFILE (ndf_Data_File,
EMPTYFILE) , 但不能清空整个FG。你需要删除或者移走这个FG中所有的Objects(tables,
indexes, even files),最后再ALTER DATABASE DBNAME REMOVE FILEGROUP
FileGroupName
·
DBCC ShrinkFile works at the extent
level. Sometimes empty pages scatter on the non-empty extents. In this case,
DBCC ShrinkFile does not help too much. You need to rebuild the clustered
index. If no CI, you need to create one, then run DBCC ShrinkFile.
·
但如果Extent里面是Varbinary(text,image)类型的数据,重建索引也没用。这时需要把碎片过多的Objects找出来(如Table)。重建它们。具体做法见:https://support2.microsoft.com/kb/324432?wa=wsignin1.0
8.6. 日志文件不停地增长 362
8.6.1. 为什么会不停增长?
·
Recovery Model is FULL
or Bulk_Logged, and no log backup for a while
·
Has an open
transaction for a long time
·
一个很大的事务在运行如建立或重建索引(get logged!),DML Modifications, an
open cursor etc. (Note: Log contains information about all of the transactions
including data modifications)
·
Transactional Replication or DB
Mirroring does not work normally.
8.6.2. 如何排查原因?
·
What is the reuse status?
-- find the log size and
used %
dbcc sqlperf(logspace)
GO
select name, recovery_model_desc, log_reuse_wait,log_reuse_wait_descffrom sys.databases
go
·
Who caused the earliest open
transaction and what does the transaction do? (注意DBCC OPENTRAN –显示的是最早的而不是最近的)
--Get the spid for the
oldest transaction
dbcc opentran
GO
--With the identified spid
for the oldest open transaction, we can find the command it issued
SELECT st.text,t2.*
from
sys.dm_exec_sessions as t2,
sys.dm_exec_connections as t1
CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(t1.most_recent_sql_handle) AS st
where t1.session_id = t2.session_id and t1.session_id >50
·
What can you do if log file is
almost full? – It depends on. Some possible actions:
o
Back it up
o
Commit the tran
o
Kill the spid
o
Switch to Simple
o
Disable the Replication or DB
Mirroring
8.7. 文件自动增长和自动收缩 367
8.7.1. 提前规划,避免自动增长,设置最大值,用Size不用百分比。
8.7.2. 多数据文件时,要尽量保证每个文件有相同的free
space。自动增长后,就只写入一个文件了。I/O分散功能消失。
8.7.3. 对日志文件,一次只写一个,多文件没帮助。
8.7.4. 慎用自动收缩(其实是DBCC
ShrinkFile)
·
产生碎片
·
治标不治本 – 还是要找出为什么自动增长的原因
·
浪费资源,影响性能
8.8. 小结 370